Behavioral targeting
For each engagement in your campaign, you can determine if a particular visitor's action or behavior will cause the messaging or chat button to display by creating behavioral targeting rules.
The default option, All behaviors, means that the button is displayed at all times and displays immediately when the page is loaded.
Which users should you target?
Consumers who show intent to purchase higher-value products or services are known as high-stakes consumers. You don’t want to forfeit any high-stakes consumers because they didn’t get the support they needed to complete a transaction. On the other hand, your agent resources are valuable and it is important to ensure they are utilized wisely, with your high-stakes consumers. So, users who are browsing free or very low-value products will not be targeted for live engagement, whereas users who show intent to carry out a high-value purchase should be engaged with an agent.
How can you target these users?
The Conversational Cloud allows you to accurately pinpoint those consumers that you want to include (or exclude from) your targeting. Let’s look at the different options for targeting particular user behaviors.
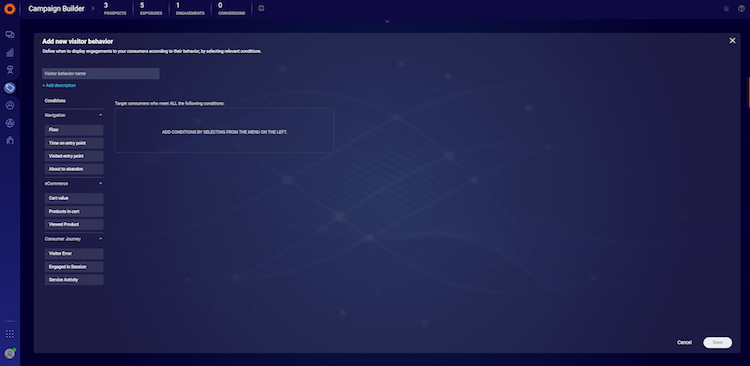
Decide when to display engagements by selecting conditions that will be applied to your users’ behavior.
Here is a list of the currently available conditions:
1. Flow
Identify consumers based on a predefined browsing pattern within your website or mobile. The flow, which is a series of at least two steps taken by the consumer, can be defined in two ways:
- Web engagements can be defined by page (URL/title) or by the section on your webpage (engagement attributes)
- Mobile engagements can be defined by sections (engagement attributes) only
Within a flow, it is possible to mark whether each step is required or not. If a step is not required, this allows the flow to have multiple routes. Engagements can be triggered when a consumer either abandons or revisits a defined flow. When a consumer abandons a flow, they do not complete all the steps of the flow (and navigate elsewhere on the site), when they revisit a flow, they go back one or more steps in the defined flow (backflow). You can find further information on targeting according to the flow below.
2. Time on the entry point
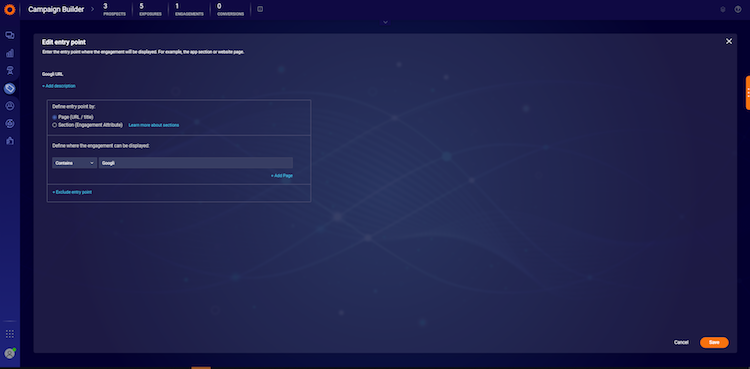
Target consumers who have spent more than the defined time in selected entry point(s) during a single session. An entry point is a location on your website (defined by a page URL or title, or a page section) or a section within your mobile app (defined by engagement attribute).
To define an entry point behavior, you can select from your existing entry points (or add a new one) and configure the amount of time in seconds that the visitor spends on this entry point after which they will be eligible to view an engagement. It is also possible to configure multiple rules for time on entry point; the engagement will only be displayed to consumers once they have met all of the rule criteria.
Note: this behavior is currently only supported for web engagements.
3. Visited entry point
Target and/or exclude consumers from selected entry points on the website or within the mobile app. To define an entry point (see above) behavior, you can select from your existing entry points (or add a new one); when a consumer lands on this entry point(s), they will be eligible to view an engagement. It is also possible to configure multiple rules for entry points visited; the consumer will only be eligible to view an engagement once they have met all of the rule criteria.
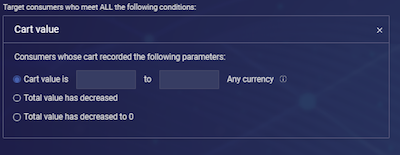
4. Cart value
Target consumers according to the value of their shopping cart. Visitors can be targeted by their cart value in three ways:
- Their cart value is between two defined parameters (in any currency) - for example, ‘Cart value is 50 to 100’
- The total value of their cart has decreased
- The total value of their cart has decreased to 0
Cart value is reported via the Cart Update Engagement Attribute; for more information on reporting this attribute, please refer to the relevant section in the Engagement Attributes guide on the Developer Center.
5. Products in cart
In order to target consumers who are interested in a specific product or type of product, you can configure an engagement to appear when they add a product(s) to their cart. The product can be defined by name, unique product identifier/stock-keeping unit (SKU), or by category name. You can also exclude engagements from appearing when these products are added to the cart.
Products in Cart are reported via the Cart Update Engagement Attribute, for more information on reporting this attribute, please refer to the relevant section in the Engagement Attributes guide on the Developer Center.
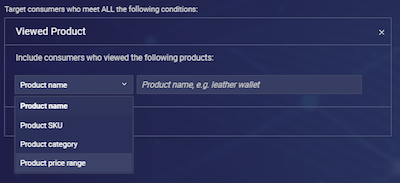
6. Viewed product
In order to target consumers who are interested in a specific product or type of product, you can configure an engagement to appear when they view a particular product. The product can be defined by name, unique product identifier/stock-keeping unit (SKU), category name, and product price range. You can also exclude engagements from appearing when they view these products.
Viewed Product is an Engagement Attribute; for more information on reporting this attribute, please refer to the relevant section in the Engagement Attributes guide on the Developer Center.
7. Visitor error
Target consumers who experience specific errors during their time on your site or mobile app. The error can be defined by a specific error message (and from which instance the consumer encounters the error e.g. first, or second) or by error code. You can also exclude engagements from appearing when they encounter a specific error(s).
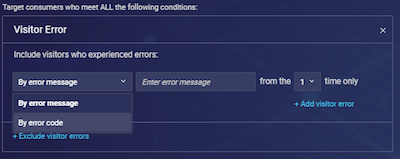
Visitor Error is an Engagement Attribute; for more information on reporting this attribute, please refer to the relevant section in the Engagement Attributes guide on the Developer Center.
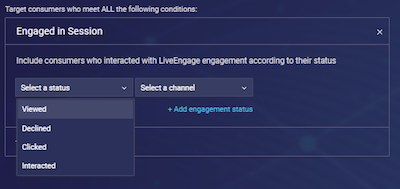
8. Engaged in session
Target consumers who interacted with engagements according to their status:
- Exposed - the consumer has previously viewed another engagement
- Declined - the consumer has previously closed another engagement
- Clicked - the consumer has previously clicked on another engagement
- Interacted - the consumer has previously clicked on another engagement and initiated a conversation (Note that for content engagements, the ‘clicked’ and ‘interacted’ statuses are the same)
You can also exclude engagements from appearing based on one or more of the above statuses.
9. Service activity
Target consumers by their service journey topics. A service journey is a series of key actions taken by a consumer when using your website or mobile app. A service journey, such as ordering a checkbook or software usage, can be measured using a service activity engagement attribute. In order to define the service activity behavior, enter the service topic name e.g. order checkbook, and define the status of the topic from the following:
- Complete
- In Progress
- Approved
- Canceled
- Not Approved
- Reviewed
- Missing Details
- Closed
- Removed
- Assigned
- Waiting for Customer Response
- Waiting for Response
- Pending
- Resolved
Service Activity is an Engagement Attribute; for more information on reporting this attribute, please refer to the relevant section in the Engagement Attributes guide on the Developer Center.
Once you’ve selected and configured your conditions, LivePerson will track and target the consumers that you most want to engage with. The more information you provide the system, the better your business results will be. Use the Behavior Conditions to improve your targeting and see an immediate boost in your ROI. Below is an example of how to target based on the user behavior type: flow.
Use case: Target users according to journey flow
Defining an accurate flow - the sequence of steps a consumer takes on their journey - is vital to effective consumer targeting. A well-planned flow enables brands to catch consumers with a relevant engagement at just the right moment when they are about to convert.
For example, a consumer may start the checkout process but decide to abandon their shopping cart. Or a user going through a defined process for registering for your newsletter or requesting a loan may give up halfway through. Once you have defined the expected flow for these journeys, you can target consumers who did not browse through all the required steps in the flow, those who browsed to a page or section outside the flow, and/or those who browsed from a later step to an earlier one. This gives you an opportunity to engage consumers and help them complete that process.
Flows can be defined either using sections (for all engagement sources) or individual URLs (for web). This allows brands to choose whether to target consumers on specific website pages or app sections. This ability to pinpoint steps in the consumer journey and guide consumers through the process means even more effective engagement and improved outcomes for the brand.
How to define a new flow
1. When adding a new engagement or editing an existing one, one of the steps you will come across is “Behavioral targeting library.”
2. Under the “Navigation” category choose “Flow.”
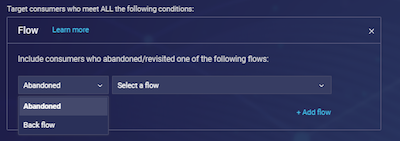
3. In order to add a new flow, open the Flow dropdown menu and select Add new flow.
4. Define your new flow by “Page (URL/title)” or by “Section (engagement attributes),” add your required parameters and click save.
5. After saving the flow, it will appear in the flows list.
6. Choose the desired behavioral targeting from the list (Abandoned or Backflow):
7. Click to save behavioral targeting.
Configuring engagements for visitor backflow
On most occasions, you expect/desire your web visitors to follow a certain flow/path on your website. For example, if you have an online shopping site, you would like your visitors to complete a purchase by following a flow such as the following:
Shopping Cart page > CheckOut page > Purchase Confirmation page
If the visitor does not complete the desired flow, the visitor exhibits what we call Back Flow Behavior. In the sample flow above, the visitor would exhibit Back Flow Behavior if they begin on the shopping cart page, proceed to the CheckOut page but then do not proceed to the purchase confirmation page. Instead, they either go back to the shopping cart page or to another page on your website, as follows:
Shopping Cart page > CheckOut page > Shopping Cart page
To manage such scenarios, you can set the Conversational Cloud to trigger an engagement (Overlay, Sticky Chat Button, etc.) whenever the system recognizes Visitor Back Flow by configuring the Behavioral Targeting for an engagement.
To set up an Engagement for Visitor Back Flow:
- Log in to the Conversational Cloud as a Campaign Manager or Admin user.
- Go to the Campaign Builder.
- Click the Campaign for which you would like to configure Visitor Backflow Behavior.
- Under the engagement that you want to configure, click Behavioral Targeting.
- After accessing the Behavioral Targeting Library, choose either to edit a rule or create a new behavioral targeting rule.
- Click Flow.
- Notice that the default selection is set to Abandoned. Click it and select Back Flow from the drop-down menu.
- Click + Add Flow and add the URLs to all the pages that you expect a visitor to browse in the order expected to complete the desired flow.
- Save the changes and publish the campaign.
Behavioral targeting conditions
Some of the targeting conditions only support web engagements. You can refer to the full list of supported conditions below to see which conditions are supported in mobile and which are not.
| Conditions | Relevant source |
| Flow | Web, Mobile |
| Time on location (entry point) | Web |
| Visited location (entry point) | Web, Mobile |
| Cart value SDE | Web, Mobile |
| Products in cart SDE | Web, Mobile |
| Viewed Product SDE | Web, Mobile |
| Visitor Error SDE | Web, Mobile |
| Engaged in Session | Web, Mobile |
| Service Activity SDE | Web, Mobile |
Missing Something?
Check out our Developer Center for more in-depth documentation. Please share your documentation feedback with us using the feedback button. We'd be happy to hear from you.